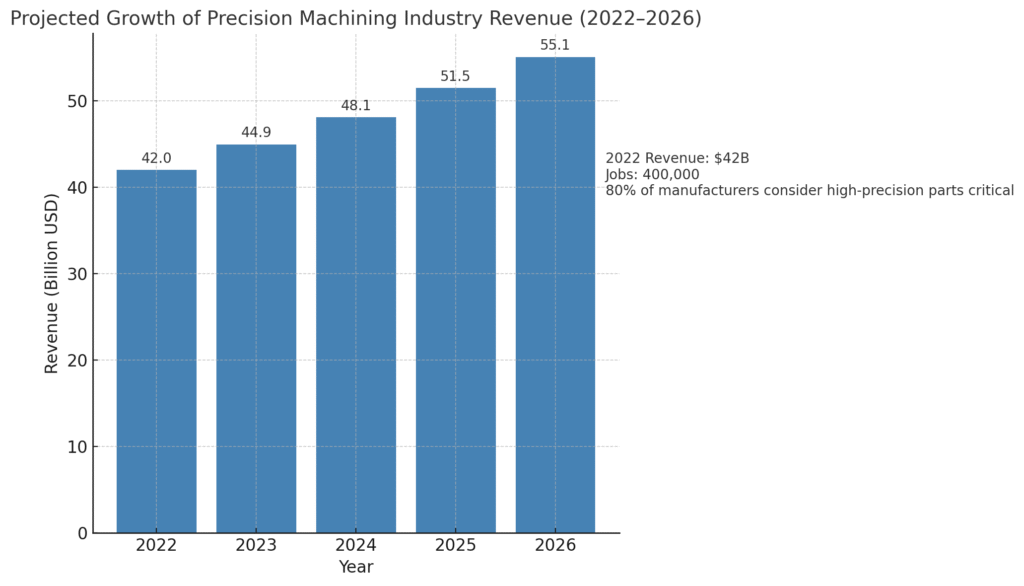
Precision machining plays a critical role in the competitiveness and operational success of U.S. businesses, particularly in the aerospace, automotive, medical device, and defense sectors. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, in 2022, the machining and precision machining industry generated $42 billion in revenue and provided more than 400,000 jobs nationwide.
Additionally, a recent report by the National Association of Manufacturers emphasized that 80 percent of manufacturers consider high-precision parts to be critical to maintaining product quality and customer satisfaction. With the growing demand for tighter tolerances and advanced materials, investment in precision machining technologies is expected to grow at a rate of 7 percent per year through 2026, underscoring the importance of precision machining technologies in the modern manufacturing ecosystem.
What is Precision Machining?
Precision machining has solidified its position as a cornerstone of advanced manufacturing in 2025. This sophisticated subtractive manufacturing discipline blends the expertise of highly trained engineers and machinists with cutting-edge, digitally integrated equipment to produce components featuring exceptionally intricate geometries and exceptionally tight tolerances. Essential for the development of critical parts across aerospace, electronics, medical device, and energy industries, precision machining enables the creation of high-performance products that define modern technological progress.
Core Methods in Precision Machining
Today, precision machining is synonymous with innovative automation and digital integration. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology drives the majority of precision machining processes, leveraging advanced algorithms and real-time feedback systems to surpass the accuracy and repeatability of conventional manual methods.
Digital Design & CNC Workflow Precision machining workflows begin with engineers developing part models using state-of-the-art Computer-Aided Design (CAD) platforms. These digital schematics are converted into instructions through Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, which programs modern CNC machines. The machines autonomously perform a vast array of processes—including milling, turning, drilling, tapping, and boring—capable of executing complex toolpaths and maintaining micron-level accuracy.
Multi-Axis CNC Machining Multi-axis CNC machining represents the industry benchmark for achieving both geometric complexity and efficiency. While foundational CNC machines operate across the X, Y, and Z axes (3-axis models), the latest precision manufacturing facilities routinely utilize 4, 5, and even up to 9-axis machining centers. The addition of rotational (A/B/C) axes enables simultaneous multi-face machining, superior surface finishes, and the elimination of secondary setups or repositioning—dramatically reducing error margins and setup times.
Industries such as medical device manufacturing, aerospace engineering, and power generation depend on multi-axis CNC machining for intricate, high-precision components where tolerance requirements are often within the range of ±0.0001 inches (±2.5 microns).
Swiss-Type Precision Machining Swiss-type CNC machining has become the technology of choice for ultra-precision, small-diameter components. By feeding the material through a guide bushing directly adjacent to the cutting tool, Swiss machines minimize deflection and vibration, achieving tolerances as tight as ±0.00005 inches (±1.3 microns). With the integration of Industry 4.0 automation, these machines are capable of unattended, lights-out operation, significantly boosting throughput and scalability for high-volume production runs.
This process is indispensable for manufacturing miniature, high-quality parts required in fields such as surgical instrumentation, micro-electronics, aerospace components, custom fasteners, and robotic assemblies.
Precision Machining Applications and Industry Standards
Modern precision machining surpasses conventional CNC abilities, delivering parts that satisfy stringent quality and performance standards required for mission-critical applications. Key attributes include:
- Ultra-Tight Tolerances: Industry-leading equipment consistently achieves tolerances down to ±0.00005″ (1.3 microns) for demanding use cases.
- Consistent Repeatability: State-of-the-art inspection and metrology systems (including CMM and in-line laser measurement) ensure repeatable production—part after part, lot after lot.
- Flexible Production Scalability: Precision machining now spans from rapid prototyping and low-volume runs to full-scale, automated 24/7 high-volume manufacturing with digital traceability.
Material Capabilities
Today’s precision machining supports an expanded range of advanced materials engineered to meet evolving technical and regulatory requirements:
- Aerospace-grade titanium, Inconel, and exotic nickel alloys
- Medical implantable stainless steels and superalloys
- Conductive copper, brass, and engineered plastics for electronics
- High-strength tool steels and heat-resistant materials for energy & automotive sectors
Partner with Mekalite for Unmatched Precision Machining
Ready to elevate your project with world-class precision, reliability, and innovation? Contact Mekalite today to discover how our advanced machining solutions can drive your success in 2025 and beyond.
Request a quote or reach out to our expert team—let’s shape the future together.




